-

What Is Poisson Distribution?
What Is Poisson Distribution Table Of Contents: What Is Poisson Distribution? Formula For Poisson Distribution. Diagram Of Poisson Distribution. Examples Of Poisson Distribution. (1) What Is Poisson Distribution? A Poisson Distribution is a discrete probability distribution. It gives the probability of an event happening a certain number of times (k) within a given interval of time or space. The Poisson Distribution has only one parameter, λ (lambda), which is known constant mean rate. We must know from the history about the mean or average value of that event. (2) Formula For Poisson Distribution. e is Euler’s number (e = 2.71828…) x is the number of occurrences
-

What Is Bernoulli Distribution?
What Is Bernoulli Distribution? Table Of Contents: What Is Bernoulli Distribution? Formula For Bernoulli Distribution. Diagram For Bernoulli Distribution. Examples Of Bernoulli Distribution. What Is A Bernoulli Trail? Difference in Binomial and Bernoulli Distribution. (1) What Is Bernoulli Distribution? Bernoulli Distribution applies to events that have one trial and two possible outcomes. Bernoulli Distribution is a discrete probability distribution, meaning it’s concerned with discrete random variables. A discrete random variable is one that has a finite or countable number of possible values—the number of heads you get when tossing three coins at once, or the number of students in a class. (2) Formula
-
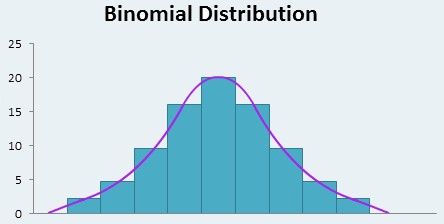
What Is Binomial Distribution?
What Is Binomial Distribution? Table Of Contents: What Is Binomial Distribution? Formula For Binomial Distribution. Diagram For Binomial Distribution. Examples Of Binomial Distribution. (1) What Is Binomial Distribution? The Binomial Distribution is the discrete probability distribution that gives only two possible results in an experiment, either Success or Failure. For example, if we toss a coin, there could be only two possible outcomes: heads or tails, and if any test is taken, then there could be only two results: pass or fail. Binomial Distribution is the extension of Uniform Distribution because in Uniform Distribution you will do the experiment only once and
