-
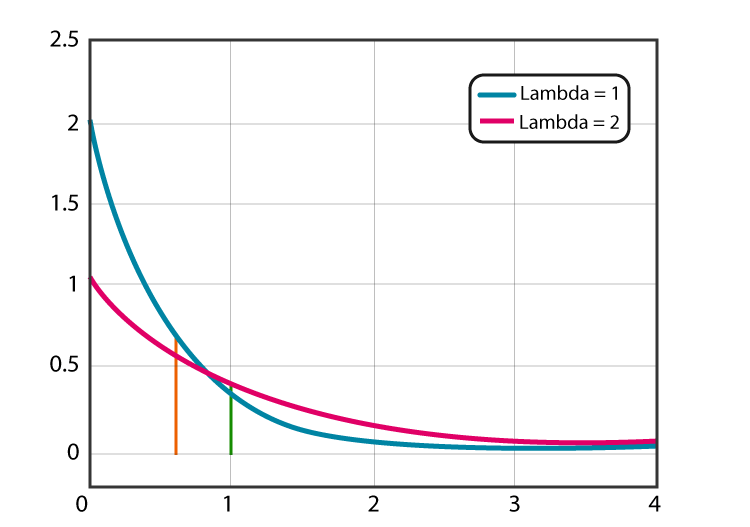
What Is Exponential Distribution?
What Is Exponential Distribution? Table Of Contents: What Is Exponential Distribution? Formula For Exponential Distribution. Diagram For Exponential Distribution. Examples Of Exponential Distribution. (1) What Is Exponential Distribution? The Exponential Distribution is a continuous distribution that is commonly used to measure the expected time for an event to occur. For example, in physics, it is often used to measure radioactive decay. In engineering, it is used to measure the time associated with receiving a defective part on an assembly line. In finance, it is often used to measure the likelihood of the next default for a portfolio of financial assets. For
-
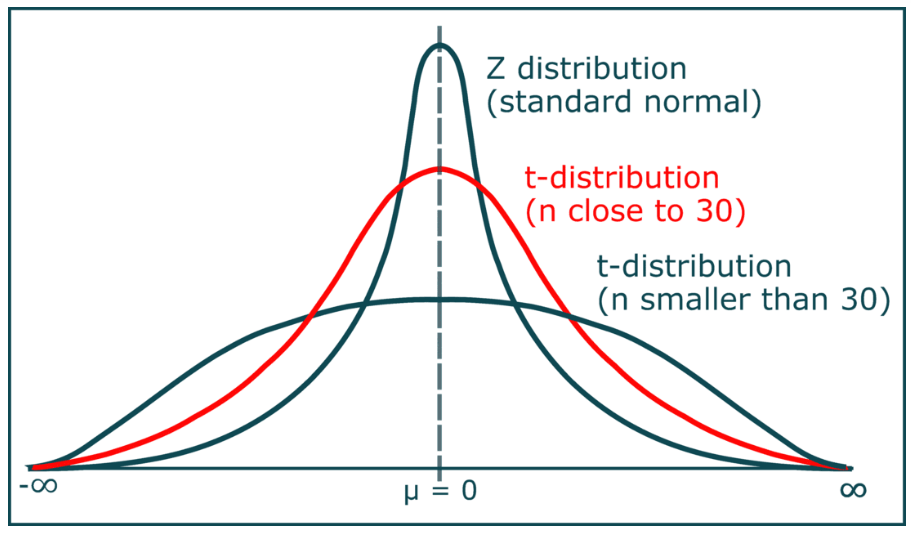
What Is Student T Distribution ?
What Is Student’s T – Distribution? Table Of Contents: What is Student’s T – Distribution? Formula For Student’s T – Distribution. Diagram For Student’s T – Distribution. Examples Of Student’s T – Distribution. (1) What Is Student’s T – Distribution? Student’s t-distribution, also known as the t-distribution, is a continuous probability distribution that is used in statistics for making inferences about the population mean when the sample size is small or when the population standard deviation is unknown. It is similar to the standard normal distribution (Z-distribution), but it has heavier tails. The t-distribution is used instead of the normal
-
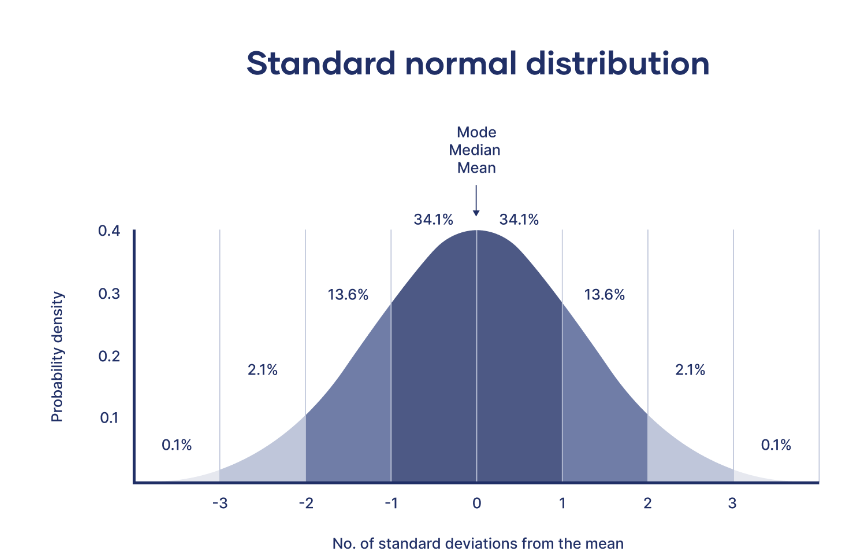
What Is Standard Normal Distribution?
What Is Standard Normal Distribution? Table Of Contents: What Is Standard Normal Distribution? Formula For Standard Normal Distribution. Diagram For Standard Normal Distribution. Examples Of Standard Normal Distribution. (1) What Is Standard Normal Distribution? The standard normal distribution, also called the z-distribution, is a special normal distribution where the mean is 0 and the standard deviation is 1. Every normal distribution is a version of the standard normal distribution that’s been stretched or squeezed and moved horizontally right or left. While individual observations from normal distributions are referred to as x, they are referred to as z in the z-distribution. Every normal distribution can be converted
