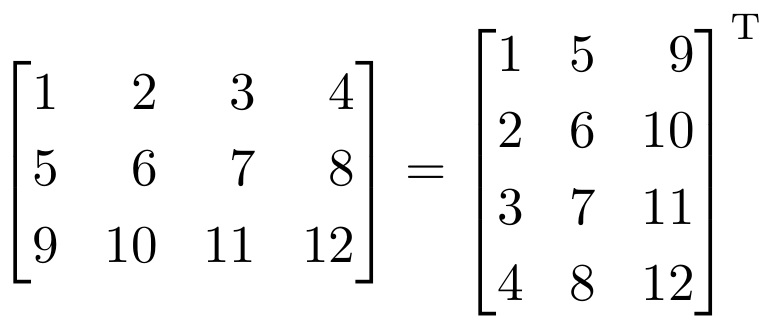Transposing And Reshaping A Matrix
Table Of Contents:
- arr.reshape(),
- arr.transpose(),
- arr.T
(1) arr.reshape()
Syntax:
numpy.reshape(a, newshape, order='C')Parameters:
- a:array_like – Array to be reshaped.
- newshape: int or tuple of ints – The new shape should be compatible with the original shape. If an integer, then the result will be a 1-D array of that length. One shape dimension can be -1. In this case, the value is inferred from the length of the array and remaining dimensions.
- order{‘C’, ‘F’, ‘A’}, optional –
Read the elements of a using this index order, and place the elements into the reshaped array using this index order. ‘C’ means to read / write the elements using C-like index order, with the last axis index changing fastest, back to the first axis index changing slowest. ‘F’ means to read / write the elements using Fortran-like index order, with the first index changing fastest, and the last index changing slowest. Note that the ‘C’ and ‘F’ options take no account of the memory layout of the underlying array, and only refer to the order of indexing. ‘A’ means to read / write the elements in Fortran-like index order if a is Fortran contiguous in memory, C-like order otherwise.
Returns:
- reshaped_array: ndarray –
This will be a new view object if possible; otherwise, it will be a copy. Note there is no guarantee of the memory layout (C- or Fortran- contiguous) of the returned array.
Example-1
import numpy as np
data = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6])
data.reshape(2, 3)Output:
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])Example-2
import numpy as np
data = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6])
data.reshape(3, 2)Output:
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]])(2) arr.transpose()
Syntax:
numpy.transpose(a, axes=None)Parameters:
- a: array_like – Input array.
- axes: tuple or list of ints, optional – If specified, it must be a tuple or list which contains a permutation of [0,1,…,N-1] where N is the number of axes of a. The i’th axis of the returned array will correspond to the axis numbered
axes[i]of the input. If not specified, defaults torange(a.ndim)[::-1], which reverses the order of the axes.
Returns:
- p: ndarray – a with its axes permuted. A view is returned whenever possible.
Example-1
import numpy as np
data = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
data.transpose()Output:
array([[1, 4],
[2, 5],
[3, 6]])(3) numpy.ndarray.T
Syntax:
ndarray.TExample-1
import numpy as np
data = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
data.TOutput:
array([[1, 4],
[2, 5],
[3, 6]])