How To Apply Query To A DataFrame?
Table Of Contents:
- Syntax ‘query( )’ Method In Pandas.
- Examples ‘query( )’ Method.
(1) Syntax:
DataFrame.query(expr, *, inplace=False, **kwargs)Description:
- Query the columns of a DataFrame with a boolean expression.
Parameters:
expr: str –
- The query string to evaluate.
- You can refer to variables in the environment by prefixing them with an ‘@’ character like
@a + b. - You can refer to column names that are not valid Python variable names by surrounding them in backticks.
- Thus, column names containing spaces or punctuations (besides underscores) or starting with digits must be surrounded by backticks.
- (For example, a column named “Area (cm^2)” would be referenced as
`Area (cm^2)`). - Column names which are Python keywords (like “list”, “for”, “import”, etc) cannot be used.
- For example, if one of your columns is called
a aand you want to sum it withb, your query should be`a a` + b.
in place: bool – Whether to modify the DataFrame rather than creating a new one.
**kwargs – See the documentation for eval() for complete details on the keyword arguments accepted by DataFrame.query().
Returns:
- DataFrame or None : DataFrame resulting from the provided query expression or None if
inplace=True
(2) Examples Of query() Method:
Example-1
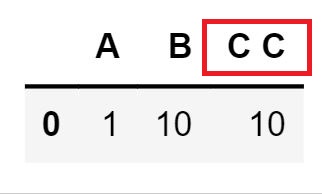
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': range(1, 6),
'B': range(10, 0, -2),
'C C': range(10, 5, -1)})
dfOutput:

df.query('A > B')Output:
The previous expression is equivalent to
df[df.A > df.B]Output:

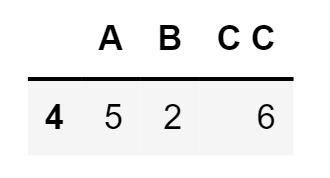
For columns with spaces in their name, you can use backtick quoting.
df.query('B == `C C`')Output: