Pandas DataFrame ‘filter( )’ Method.
Table Of Contents:
- Syntax Of ‘filter()’ Method In Pandas.
- Examples Of ‘filter( )’ Method.
(1) Syntax:
DataFrame.filter(items=None, like=None, regex=None, axis=None)Description:
Subset the dataframe rows or columns according to the specified index labels.
Note that this routine does not filter a dataframe on its contents. The filter is applied to the labels of the index.
Parameters:
- items: list-like –
- Keep labels from axis which are in items.
- like: str –
- Keep labels from axis for which “like in label == True”.
- regex: str (regular expression) –
- Keep labels from axis for which re.search(regex, label) == True.
- axis{0 or ‘index’, 1 or ‘columns’, None}, default None –
- The axis to filter on, expressed either as an index (int) or axis name (str). By default this is the info axis, ‘columns’ for DataFrame. For Series this parameter is unused and defaults to None.
Returns:
- same type as the input object
(2) Examples Of filter() Method:
Example-1
df = pd.DataFrame(np.array(([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])),
index=['mouse', 'rabbit'],
columns=['one', 'two', 'three'])
dfOutput:

# Select columns by name
df.filter(items=['one', 'three'])Output:

# Select columns by regular expression
df.filter(regex='e$', axis=1)Output:
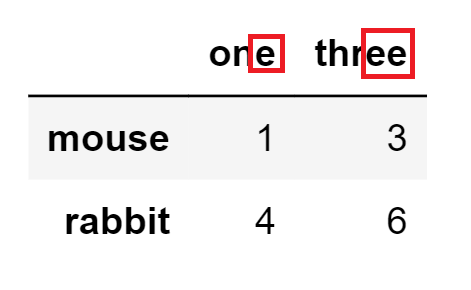
# Select rows containing ‘bbi’
df.filter(like='bbi', axis=0)Output:


