What Is Poisson Distribution
Table Of Contents:
- What Is Poisson Distribution?
- Formula For Poisson Distribution.
- Diagram Of Poisson Distribution.
- Examples Of Poisson Distribution.
(1) What Is Poisson Distribution?
- A Poisson Distribution is a discrete probability distribution.
- It gives the probability of an event happening a certain number of times (k) within a given interval of time or space.
- The Poisson Distribution has only one parameter, λ (lambda), which is known constant mean rate.
- We must know from the history about the mean or average value of that event.
(2) Formula For Poisson Distribution.
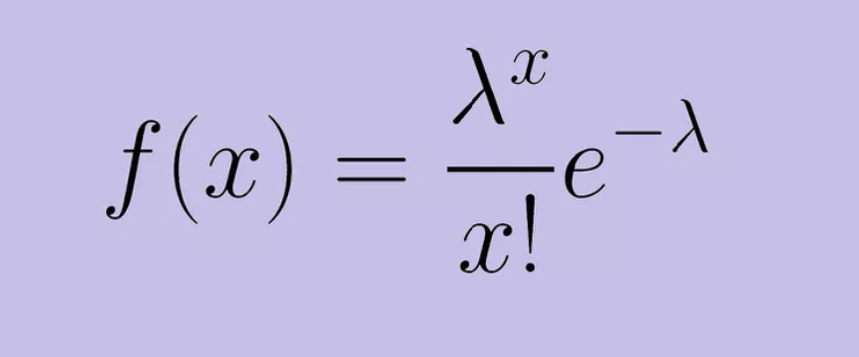
- e is Euler’s number (e = 2.71828…)
- x is the number of occurrences
- x! is the factorial of x
- λ (lambda) = mean or average value of that event.
(3) Diagram For Poisson Distribution.
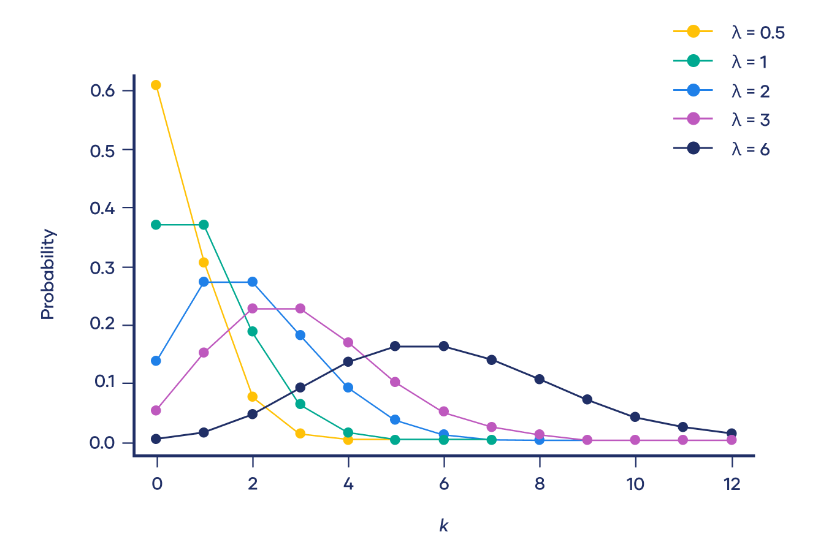
- The graph below shows examples of Poisson distributions with different values of λ.
(4) Examples Of Poisson Distribution.
Example-1:Question
- The average number of major storms in your city is 2 per year. What is the probability that exactly 3 storms will hit your city next year?
Solution:
- μ = 2 (average number of storms per year, historically)
- x = 3 (the number of storms we think might hit next year)
- e = 2.71828 (e is Euler’s number, a constant)
- P(x; λ) = (e– λ λx)/x! =
- (2.71828 – 2) (23) / 3!
- = (0.13534) (8) / 6
- = 0.180
- The probability of 3 storms happening next year is 0.180, or 18%
Example-2:Question
- Telephone calls arrive at an exchange according to the Poisson process at a rate λ= 2/min.
- Calculate the probability that exactly two calls will be received during each of the first 5 minutes of the hour.
Solution:
Assume that “N” be the number of calls received during a 1 minute period.
Therefore,
P(N= 2) = (e-2. 22)/2!
P(N=2) = 2e-2.
Now, “M” be the number of minutes among 5 minutes considered, during which exactly 2 calls will be received. Thus “M” follows a binomial distribution with parameters n=5 and p= 2e-2.
P(M=5) = 32 x e-10
P(M =5) = 0.00145, where “e” is a constant, which is approximately equal to 2.718.

