What Is Uniform Distribution?
Table Of Content:
- What Is Uniform Distribution?
- Formula For Uniform Distribution.
- Example Of Uniform Distribution.
(1) What Is Uniform Distribution?
- In statistics, uniform distribution refers to a type of probability distribution in which all outcomes are equally likely.
- A deck of cards has within it uniform distributions because the likelihood of drawing a heart, a club, a diamond, or a spade is equally likely.
- A coin also has a uniform distribution because the probability of getting either heads or tails in a coin toss is the same.
- The uniform distribution can be visualized as a straight horizontal line, so for a coin flip returning a head or tail, both have a probability p = 0.50 and would be depicted by a line from the y-axis at 0.50.
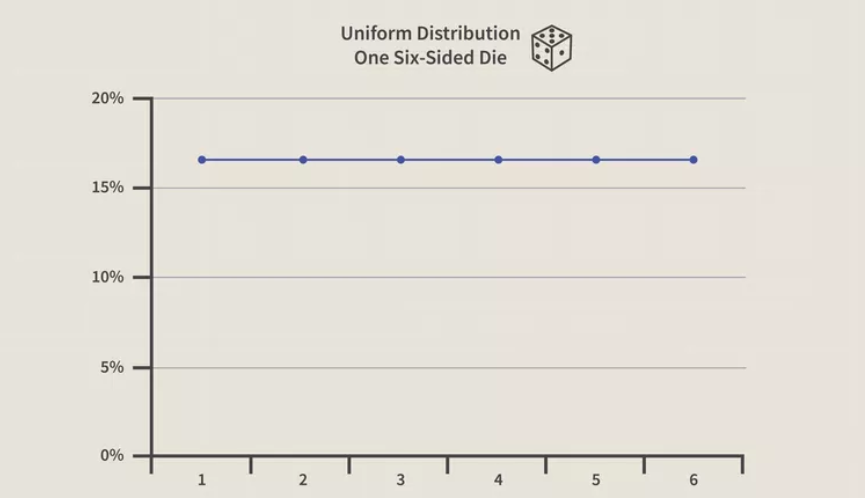
Uniform Distribution of one six-sided die
(2) Types Of Uniform Distribution?
- There are two types of uniform distributions: discrete and continuous.
- The possible results of rolling a die provide an example of a discrete uniform distribution: it is possible to roll a 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6, but it is not possible to roll a 2.3, 4.7, or 5.5.
- Therefore, the roll of a die generates a discrete distribution with p = 1/6 for each outcome.
- There are only 6 possible values to return and nothing in between.
(3) Formula For Continuous Uniform Distribution?
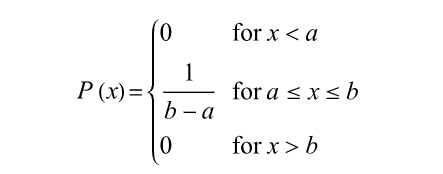
- This Probability Density Function is applicable to continuous variables.
- For Discrete Variables like rolling a die, the probability function will be different.
- This distribution is defined by two parameters, a and b:
- a is the minimum.
- b is the maximum.
- The distribution is written as U(a, b).

- The following graph shows the distribution with a = 1 and b = 3:
- Like all probability distributions for continuous random variables, the area under the graph of a random variable is always equal to 1.
- A = l x h = 2 * 0.5 = 1.
(3) Formula For Discrete Uniform Distribution?

(4) Examples Of Discrete Uniform Distribution?
- As with the example of the die, each side contains a unique whole number. The probability of rolling the die and getting any one number is 1/6, or 16.67%.
(5) Examples Of Continuous Uniform Distribution?
Example-1
There are 52 cards in a traditional deck of cards. In it are four suits: hearts, diamonds, clubs, and spades. Each suit contains an A, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, J, Q, K, and 2 jokers. However, we’ll do away with the jokers and face cards for this example, focusing only on number cards replicated in each suit. As a result, we are left with 40 cards, a set of discrete data.
Suppose you want to know the probability of pulling a 2 of hearts from the modified deck. The probability of pulling a 2 of hearts is 1/40 or 2.5%. Each card is unique; therefore, the likelihood that you will pull any one of the cards in the deck is the same.
Now, let’s consider the likelihood of pulling a heart from the deck. The probability is significantly higher. Why? We are now only concerned with the suits in the deck. Since there are only four suits, pulling a heart yields a probability of 1/4 or 25%.
Example-2
- Some uniform distributions are continuous rather than discrete. An idealized random number generator would be considered a continuous uniform distribution.
- With this type of distribution, every point in the continuous range between 0.0 and 1.0 has an equal opportunity of appearing, yet there is an infinite number of points between 0.0 and 1.0.
